Diallyl Dimethyl Ammonium Chloride, commonly known as DADMAC, is a powerful cationic monomer used in a wide variety of industrial processes, from water purification to cosmetics. Despite its complex name, DADMAC plays a simple but crucial role in many chemical formulations.
This beginner’s guide offers an in-depth look at what DADMAC is, how it’s made, why it’s unique, where it’s used, and how to handle it safely. Let’s explore the world of this versatile compound.
Understanding the Chemical Structure of DADMAC
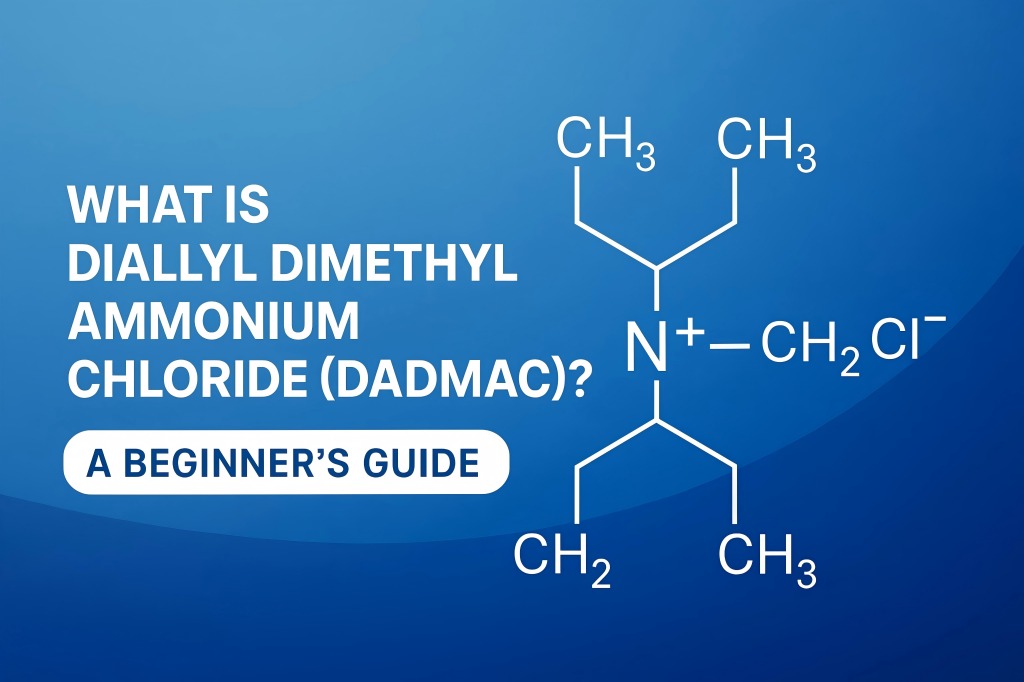
DADMAC has the molecular formula C8H16ClN, making it a quaternary ammonium salt. It consists of a nitrogen atom bonded to two methyl groups and two allyl groups, giving it a strong positive charge. The nitrogen atom is permanently charged, making DADMAC a cationic (positively charged) monomer, and the chloride ion (Cl⁻) serves as a counterion.
This structure allows DADMAC to interact with negatively charged particles in water, textiles, paper, and other materials. The double allyl groups also make it polymerizable, meaning it can form larger molecules (polymers) such as PolyDADMAC, which are widely used in industry.

How DADMAC Is Synthesized: An Overview of Production Methods
Producing DADMAC involves a two-step chemical reaction sequence:
Step 1: Alkylation of Dimethylamine
Dimethylamine is reacted with allyl chloride to produce allyl dimethylamine, a key intermediate. Because of the components’ reactivity, this procedure necessitates precise temperature and pressure control.
Step 2: Quaternization
The allyl dimethylamine is then further reacted with another equivalent of allyl chloride to form Diallyl Dimethyl Ammonium Chloride through a quaternization reaction. This step converts the neutral amine into a permanently charged quaternary ammonium compound.
Finally, the resulting product is filtered, refined, and diluted to various concentrations (60–90%) to meet industrial specifications. Depending on the end-use, manufacturers may adjust purity levels, stabilizers, and packaging formats.
Key Physical and Chemical Properties of DADMAC
Understanding DADMAC’s behavior in chemical systems starts with its physical and chemical traits. Here is a snapshot:
| Property | Value / Description |
| Chemical Name | Diallyl Dimethyl Ammonium Chloride |
| Chemical Formula | C8H16ClN |
| Molecular Weight | ~161.67 g/mol |
| Appearance | Clear to pale yellow liquid |
| Odor | Mild amine-like |
| Solubility | Completely soluble in water |
| pH (1% aqueous solution) | 5.0 – 7.0 |
| Charge Density | Very high (strong cationic character) |
| Flash Point | > 110°C |
| Boiling Point | Decomposes above 100°C |
These properties make DADMAC ideal for use in aqueous formulations, especially in water treatment and polymer manufacturing.
What Makes DADMAC a Unique Cationic Monomer?
DADMAC stands out among cationic monomers for several reasons:
- Extremely High Charge Density: One of the highest among all water-soluble cationic monomers. This enables negatively charged particles to be neutralized quickly.
- Excellent Water Solubility: Unlike some cationic compounds that are only dispersible, DADMAC dissolves completely, improving compatibility in formulations.
- Stable Chemical Nature: Its quaternary ammonium structure is resistant to oxidation and hydrolysis, enhancing shelf life and performance.
- Polymerization Versatility: It can be homopolymerized or copolymerized with acrylamide, acrylates, and other vinyl monomers to produce a range of flocculants, thickeners, and antistatic agents.
Its chemical profile makes DADMAC highly desirable in industries that require fast and effective interactions with negatively charged substances—especially in large-scale water and waste processing.
Major Industrial Applications of DADMAC
DADMAC is a workhorse monomer used across many industries. Below are its most common applications:
Water and Wastewater Treatment
The treatment of wastewater in cities and industries is one of DADMAC’s most important applications. It is polymerized into PolyDADMAC, a cationic flocculant used to remove suspended solids, organics, algae, and turbidity from water.
Papermaking
DADMAC-based polymers serve as retention and drainage aids. They help fine particles and fillers stick to paper fibers, enhancing sheet strength and reducing waste. They also contribute to wet strength additives, which improve durability when paper is exposed to moisture.
Textile Industry
DADMAC is used as an antistatic and dye-fixing agent in textiles. It helps set dyes permanently onto fabric and minimizes electrostatic charge buildup, particularly in synthetic fibers.
Oilfield and Petrochemical
DADMAC plays a role in emulsion breaking, sludge dewatering, and oil–water separation processes. Its polymers work especially well in drilling mud compositions and enhanced oil recovery.
Cosmetics and Personal Care
DADMAC is utilized in hair conditioners, lotions, and creams within the cosmetics business. Its cationic properties contribute to a softer, smoother sensation for skin and hair.
Paints, Coatings, and Adhesives
Cationic latex polymers using DADMAC offer improved adhesion, clarity, and water resistance. They are especially useful in coating systems for paper and plastics.
Grades and Concentrations of DADMAC Available on the Market
Depending on the needs of the application, DADMAC is offered in a variety of concentration grades. Each grade has distinct benefits:
| Grade | Concentration | Common Uses |
| Industrial Grade | 60% | Water treatment, bulk textiles, oilfield chemicals |
| Technical Grade | 70–80% | Papermaking, retention aids, textile auxiliaries |
| High-Purity Grade | ≥90% | Cosmetics, personal care, specialty polymers requiring minimal residual monomer |
60% Grade
This grade is designed for cost-effective, high-volume applications. While it has a slightly higher impurity content, it is adequate for processes where product aesthetics and sensitivity are not critical. It is most widely used in water treatment and textile dyeing.
70–80% Grade
This intermediate grade strikes a balance between performance and economy. It is common in papermaking, industrial wastewater treatment, and coating emulsions. The higher purity offers more consistent reactivity in polymer production.
90%+ Grade
Reserved for cosmetic and pharmaceutical applications, the high-purity DADMAC grade has extremely low residuals, making it suitable for personal care products that come in contact with skin or hair. It also meets more stringent regulatory requirements like REACH or FDA.
DADMAC in Water Treatment: Mechanism of Action
DADMAC-based polymers, particularly PolyDADMAC, are widely used as primary coagulants and flocculants in water treatment systems. Here’s how they work:
Step 1: Charge Neutralization
Most contaminants in water, such as clay, organic matter, and bacteria, are negatively charged. DADMAC’s strong positive charge immediately neutralizes these charges, collapsing the colloidal structure.
Step 2: Bridging and Flocculation
Once neutralized, the polymers bridge the destabilized particles, causing them to cluster into larger aggregates, or flocs .Filtration or sedimentation are simpler methods of removing these flocs.
Step 3: Separation
The flocs formed through DADMAC coagulation settle faster due to their size and weight, leading to improved filtration efficiency, lower chemical consumption, and less sludge generation.
Advantages in Water Treatment:
- Works at a wide pH range
- Reduces need for pH adjustment chemicals
- Generates less sludge compared to alum or iron salts
- Compatible with both drinking water and industrial effluent systems
Safety and Handling Guidelines for DADMAC
Despite DADMAC’s low toxicity, handling and storage procedures must be carried out according to the right safety procedures.
Handling Precautions
- Use chemical-resistant gloves, goggles, and protective clothing.
- When working with big numbers, make sure there is enough ventilation.
- Steer clear of skin, clothing, and eyes.
Storage Guidelines
- Store in cool, dry, and well-ventilated areas.
- Steer clear of hot weather or direct sunshine.
- Use HDPE, stainless steel, or glass-lined storage tanks.
First Aid Measures
- Skin Contact: Wash right away with water and soap.
- Eye Contact: Give it a careful 15-minute water rinse.
- Inhalation: If symptoms don’t go away, get outside and visit a doctor.
- Ingestion: Get help right away; don’t make yourself throw up.
Environmental Precautions
- Avoid uncontrolled discharge into natural waterways.
- Treat effluents containing DADMAC polymers before release.
- Follow local hazardous waste disposal regulations.