Water purification is vital for safe drinking, industrial processes, and environmental health. Cationic coagulants like DADMAC and PolyDADMAC help remove solids, organics, and colloids. Though related, they differ in function and performance.
This article compares their structures, properties, uses, effectiveness, environmental impact, and regulatory status.
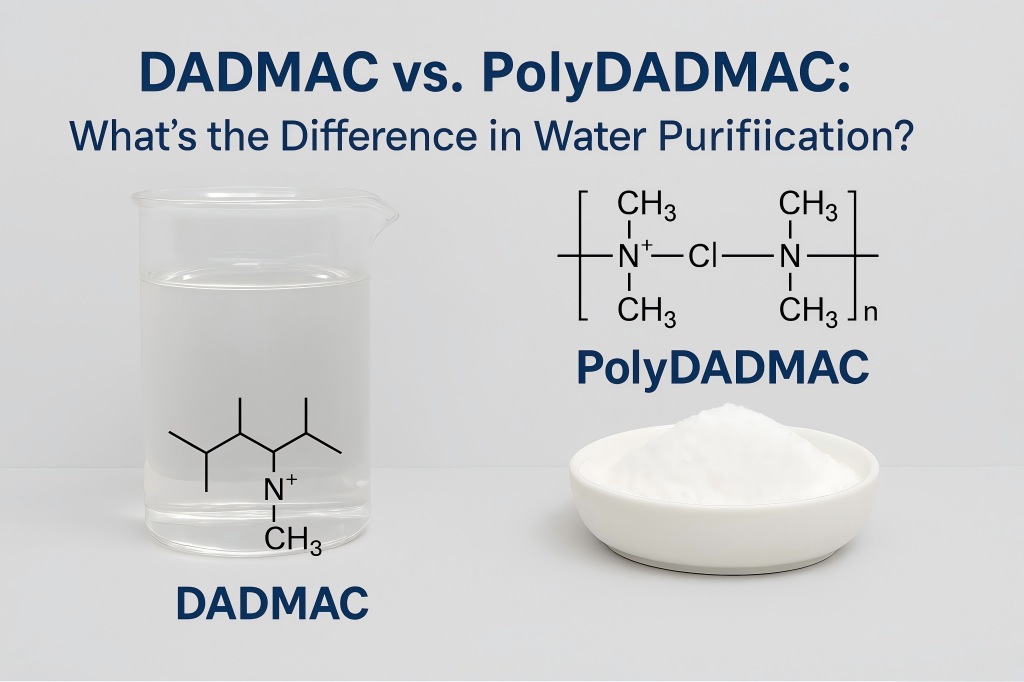
Understanding the Basics: What are DADMAC and PolyDADMAC?

DADMAC: The Monomer
The chemical formula for Diallyl Dimethyl Ammonium Chloride (DADMAC), a quaternary ammonium salt monomer, is C8H16ClN. It appears as a colorless to pale yellow liquid, highly soluble in water, and is often supplied in aqueous solutions at concentrations of 60% or higher.
Its structure features two allyl groups attached to a nitrogen atom with two methyl groups, giving it strong cationic properties. This molecular design makes DADMAC a useful precursor for polymerization reactions.
PolyDADMAC: The Polymer
A high molecular weight polymer called Polydiallyldimethylammonium Chloride (PolyDADMAC) is created when DADMAC monomers are homopolymerized. It exists in various forms, including liquid, powder, or emulsion, and exhibits a strong cationic charge density.
Its polymeric structure enhances its ability to bind and agglomerate negatively charged particles in water, making it an effective flocculant and coagulant.
Structural and Chemical Differences
| Property | DADMAC | PolyDADMAC |
| Type | Monomer | Homopolymer |
| Molecular Weight | Low (~161.5 g/mol) | High (hundreds of thousands g/mol) |
| Appearance | Colorless to light yellow liquid | Liquid, powder, or emulsion |
| Solubility | Fully water-soluble | Fully water-soluble |
| Charge Density | High (single molecule level) | Very high (multiple cationic sites) |
| Function | Building block, reactive agent | Coagulant, flocculant |
The structural difference directly impacts their behavior in water treatment. While DADMAC is reactive and mainly used for polymer production, PolyDADMAC is employed directly in treatment processes.
Functionality in Water Purification
Coagulation and Flocculation
In water treatment, coagulation refers to destabilizing suspended particles, and flocculation involves the aggregation of these destabilized particles into larger flocs. PolyDADMAC excels in both functions due to its long chain and repeated cationic groups that neutralize negative charges and bind particles together.
DADMAC, being a monomer, does not provide sufficient flocculation capacity on its own. However, it is essential in the synthesis of effective coagulants like PolyDADMAC, poly(DADMAC-acrylamide), and other copolymers.
Charge Neutralization
PolyDADMAC has a very high cationic charge density, which makes it extremely effective in neutralizing negatively charged impurities such as humic substances, clay particles, colloids, and organic matter. DADMAC contributes to this effect only when polymerized.
Compatibility
PolyDADMAC works efficiently with both organic and inorganic coagulants like alum or ferric chloride, enhancing performance and reducing sludge volumes. It is particularly beneficial in low-temperature or low-turbidity waters where conventional inorganic coagulants perform poorly.
Application Areas in Water Treatment
| Application Area | DADMAC | PolyDADMAC |
| Drinking Water Purification | Used indirectly (as monomer) | Used directly as coagulant/flocculant |
| Wastewater Treatment | Not used directly | Widely used in municipal and industrial wastewater |
| Sludge Dewatering | No application | Effective in sludge thickening and dewatering |
| Paper and Pulp Processing | Used in copolymer synthesis | Applied in retention and drainage aids |
| Textile Industry | Polymer component in dye-fixation agents | Directly used for color removal and fixing dyes |
| Oil and Gas | Used in polymeric EOR formulations | Used in produced water treatment |
Dosage and Performance Efficiency
PolyDADMAC Dosage
The properties of the raw water or wastewater determine the dosage of PolyDADMAC. Typical doses range from 1 to 15 mg/L, depending on turbidity, organic matter, and desired performance. It shows fast reaction kinetics and reduces the need for traditional inorganic coagulants, thus minimizing sludge generation.
DADMAC Dosage (in Polymer Synthesis)
In industrial polymerization, DADMAC is used at specific molar ratios depending on the desired polymer chain length and application properties. In water treatment, its relevance is indirect, influencing polymer properties such as molecular weight, solubility, and charge density.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Biodegradability
PolyDADMAC is considered non-biodegradable under standard conditions, although it tends to form stable flocs that can be separated from treated water. This raises concerns regarding sludge disposal and potential environmental accumulation.
DADMAC itself is also non-biodegradable but exhibits low toxicity and volatility, making it relatively safe to handle.
Toxicity
Both substances exhibit low acute toxicity to humans. However, their potential effects on aquatic life necessitate careful dosage control and sludge handling to prevent ecological impacts.
| Parameter | DADMAC | PolyDADMAC |
| Biodegradability | Low | Low |
| Toxicity to Humans | Low | Low |
| Aquatic Toxicity | Low to moderate (depends on concentration) | Moderate to high at improper dosages |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal if used in controlled polymer synthesis | Requires careful sludge management |
Cost and Availability
Raw Material Cost
DADMAC is relatively cost-effective as a chemical monomer and is widely available in the chemical market. PolyDADMAC, being a polymer, is more expensive due to its synthesis process, purification steps, and formulation into usable forms.
Operational Cost
Despite the higher unit cost of PolyDADMAC, its higher efficiency and reduced sludge production often make it more economical in the long term. It also reduces the need for other coagulants and minimizes post-treatment steps.
Global Regulatory and Market Status
United States (EPA, NSF)
PolyDADMAC is approved by the NSF/ANSI Standard 60 for use in drinking water treatment chemicals with specific concentration limits. DADMAC is considered a polymer precursor and must meet purity standards during polymer synthesis.
European Union (REACH)
Both DADMAC and PolyDADMAC are registered under REACH regulations. PolyDADMAC must be used according to safe handling procedures, especially in drinking water facilities.
Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, India)
PolyDADMAC is listed in water treatment regulations and environmental protection guidelines, particularly in China, where its use is widespread. Manufacturers must declare DADMAC content and ensure compliance with environmental discharge norms.
Future Trends: Sustainable and Hybrid Coagulants
Bio-Based Alternatives
Research is ongoing into replacing synthetic monomers like DADMAC with bio-based cationic polymers derived from starch, chitosan, or cellulose. These aim to enhance biodegradability and reduce environmental impact.
Hybrid Polymers
PolyDADMAC is being increasingly integrated into copolymers or hybrid materials that combine cationic and nonionic functionalities to improve performance across varying water qualities.
Nanotechnology and Advanced Materials
PolyDADMAC is also being tested as a support matrix for nanoparticle-based coagulants or as a modifier in membrane filtration systems to enhance anti-fouling properties.
Final Comparison Table: DADMAC vs. PolyDADMAC
| Feature | DADMAC | PolyDADMAC |
| Molecular Type | Monomer | Polymer |
| Function in Water Treatment | Raw material for polymers | Direct flocculant/coagulant |
| Charge Density | Single unit | Very high (polymeric chain) |
| Application Scope | Limited direct use | Widely used in purification |
| Efficiency | Not applicable | High |
| Cost per kg | Lower | Higher |
| Sludge Production | Not applicable | Lower than traditional coagulants |
| Environmental Impact | Low toxicity, non-biodegradable | Sludge management needed |
| Regulatory Approval | Required for polymer synthesis | Approved for drinking water use |