In the chemical and manufacturing industries, selecting the right solvent, humectant, or carrier fluid is essential to ensuring optimal product performance, stability, and regulatory compliance. Two compounds often compared in this regard are Propylene Glycol (PG) and Dipropylene Glycol (DPG). Though chemically related, their properties, uses, and regulatory classifications diverge significantly.
As a trusted chemical supplier with extensive expertise in both PG and DPG, we aim to clarify the similarities and differences between these compounds to help formulators and procurement teams make informed decisions tailored to their industry and application requirements.
Chemical Overview
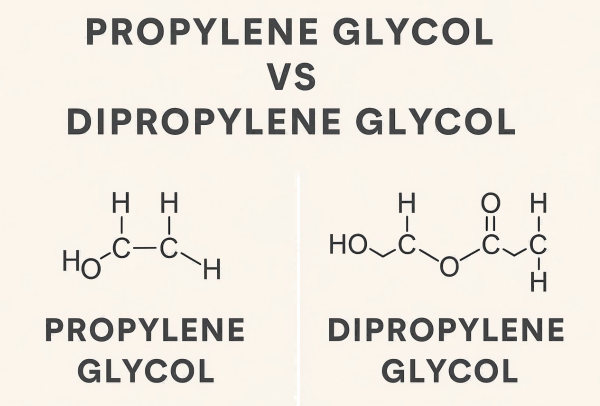
Propylene Glycol (PG)
- IUPAC Name: Propane-1,2-diol
- Chemical Formula: C₃H₈O₂
- Molecular Weight: 76.09 g/mol
- CAS Number: 57-55-6
- Structure: A simple diol with two hydroxyl (-OH) groups on adjacent carbon atoms.
Dipropylene Glycol (DPG)
- IUPAC Name: 2-(2-Hydroxypropoxy)propan-1-ol
- Chemical Formula: C₆H₁₄O₃
- Molecular Weight: 134.17 g/mol
- CAS Number: 110-98-5
- Structure: A more complex glycol composed of two propylene glycol units connected via an ether bond.
Production and Purity Grades
Manufacturing Process
PG is produced mainly by the hydration of propylene oxide. It is available in two grades: USP/Pharmaceutical grade and Industrial grade.
DPG is a by-product of PG production via condensation, leading to a mixture of isomers. It is typically offered in:
- DPG – Industrial Grade (often used in resins, plasticizers)
- DPG – Fragrance or Low-Odor Grade (used in personal care and fragrances)
Purity and Quality
| Grade | Propylene Glycol | Dipropylene Glycol |
| USP/Pharma | ≥99.5% | Not typically available |
| Industrial | ≥99.0% | ≥98.0% |
| Fragrance Grade | Rare | Low odor, ≥99.5% purity (select isomers) |
Physical and Chemical Properties
| Property | Propylene Glycol | Dipropylene Glycol |
| Appearance | Colorless, viscous liquid | Colorless, viscous liquid |
| Odor | Nearly odorless | Faint to low odor (low-odor grades available) |
| Boiling Point | ~188°C | ~230°C |
| Flash Point | ~99°C (closed cup) | ~124°C |
| Vapor Pressure | Higher | Lower (less volatile) |
| Viscosity | Lower | Higher |
| Solubility | Miscible with water and alcohols | Miscible with water and many organic solvents |
These physical differences influence how each compound behaves in formulation settings, especially in terms of evaporation, solvency, and heat stability.
Functional Differences in Application
Solvent Performance
PG is a highly efficient solvent for a wide range of active ingredients, including pharmaceuticals, food additives, and cosmetic actives.
DPG is preferred where a slower evaporation rate or more stable fragrance release is required, such as in perfumes and air fresheners.
Humectant Function
Because they both draw and hold moisture, PG and DPG are hygroscopic.
However:
PG is better suited for skin-contact applications due to extensive toxicological data and FDA approvals.
DPG is mainly used in industrial and fragrance applications where long-term moisture retention and low volatility are needed.
Carrier and Diluent Role
PG is often used as a carrier in e-liquids (vaping), injectables, and personal care creams.
DPG is commonly used to dilute fragrances, essential oils, and industrial resins due to its neutral scent and stable nature.
Industry Applications
Personal Care and Cosmetics
| Application | Preferred Glycol | Reason |
| Lotions, creams | PG | Skin safety, humectancy |
| Perfumes | DPG | Fragrance stability, low odor |
| Deodorants | Either | Depends on formula volatility |
| Hair products | PG | Fast absorption |
| Bath products | DPG | Longer-lasting scent release |
Industrial Use
DPG is widely used in
- Plasticizer production
- Unsaturated polyester resins
- Heat transfer fluids
- Brake fluids
PG is used in
- Hydraulic fluids
- De-icing solutions
- Coolants
- Lubricant bases
Food and Pharmaceutical
Propylene Glycol USP grade is FDA-approved as:
- A food additive (E1520)
- An excipient in injectable, oral, and topical drugs
Dipropylene Glycol is not used in ingestible or injectable formulations due to limited pharmacokinetic data.
Safety and Toxicology
Propylene Glycol
Oral LD50 (rat): ~20,000 mg/kg (low toxicity)
Dermal Safety: Considered non-sensitizing and non-irritating
Approved by:
- FDA (food and drug)
- EMA (cosmetic use)
- WHO (safe daily intake of 25 mg/kg body weight)
Dipropylene Glycol
- Oral LD50 (rat): ~15,000 mg/kg (also low toxicity)
- Dermal Safety: Generally safe, but some isomers may cause irritation
- Not approved for food or drug use in most countries
Environmental and Regulatory Aspects
Biodegradability
Both PG and DPG are readily biodegradable and considered low-risk for environmental accumulation.
REACH and GHS Classification
Both substances are REACH-registered in the EU and not classified as hazardous under the GHS (Globally Harmonized System).
For information on workplace exposure limits and storage requirements, one must refer to Safety Data Sheets (SDS).
Pricing and Availability
| Aspect | Propylene Glycol | Dipropylene Glycol |
| Cost per kg (bulk) | Lower | Slightly higher |
| Availability | Very high (globally) | Moderate (select markets) |
| Supply Volatility | Low | Medium (fewer manufacturers) |
As a chemical supplier, we typically recommend PG for high-volume consumer products and DPG for specialty applications where low volatility or fragrance compatibility is a must.
Selection Criteria for Buyers and Formulators
When choosing between PG and DPG, consider the following:
| Criteria | Preferred Glycol |
| Human exposure (skin or oral) | Propylene Glycol |
| Fragrance blending | Dipropylene Glycol |
| Cost sensitivity | Propylene Glycol |
| Product longevity or slow evaporation | Dipropylene Glycol |
| Regulatory clearance for ingestible use | Propylene Glycol |
| Compatibility of plasticizer or resin | Dipropylene Glycol |
Which One Should You Choose?
The choice between propylene glycol and dipropylene glycol depends largely on the end-use application, desired performance traits, and regulatory requirements. Propylene glycol is the versatile workhorse trusted across food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries due to its established safety profile and broad functionality. In contrast, dipropylene glycol offers specialized advantages for fragrance, industrial formulations, and slow-evaporation applications.
As a raw material supplier, we provide both PG and DPG in bulk quantities and offer technical guidance tailored to your product line. Whether you need a food-grade solvent or a high-performance carrier for perfume, we can match your specifications with consistent, high-purity supply.

