Reliable Surfactants Suppliers
NIRAN Chemical provides a wide range of anionic, amphoteric, cationic, and nonionic surfactants from our manufacturers, ensuring high-quality products to meet your formulation needs with reliable service and supply chain expertise.
Advantages of Choosing Us:
- Quality: High-purity surfactants
- Range: Wide product selection
- Reliability: Accurate, on-time service
- Expertise: Formulation support
- Compliance: Regulatory assistance
- Cost-efficiency: Economic solutions
- Partnership: Dedicated customer support
Types of Surfactants
Each type of surfactant has unique properties and is chosen based on specific application requirements, such as cleaning ability, mildness, foaming properties, and ingredient compatibility.

Anionic Surfactants
- Definition: These surfactants have a negatively charged hydrophilic head.
- Common Examples: Sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate.
- Uses: Widely used in laundry detergents, dishwashing liquids, and shampoos due to their excellent cleaning & foaming properties.

Cationic Surfactants
- Definition: These surfactants have a positively charged hydrophilic head.
- Common Examples: Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), benzalkonium chloride.
- Uses: Commonly used in fabric softeners, hair conditioners, and as disinfectants due to their ability to kill bacteria and other microorganisms.

Nonionic Surfactants
- Definition: These surfactants have no charge on their hydrophilic head.
- Common Examples: Ethoxylated alcohols, alkyl polyglucosides.
- Uses: Used in a variety of applications, including household cleaners, personal care products, and industrial processes, due to their mildness and effectiveness in breaking down oils and fats.

Amphoteric Surfactants
- Definition:These surfactants have both positive and negative charges on their hydrophilic head, depending on the pH of the solution.
- Common Examples: Cocamidopropyl betaine, lecithin.
- Uses: Often used in mild personal care products like baby shampoos and skin cleansers because they are less irritating to the skin & eyes.
Forms of Surfactants
Surfactants come in various forms, including liquid, powdered, granular, paste/gel, and solid, each suited to specific applications and performance requirements.
Liquid Surfactants
- Advantages: Easy to mix and apply, high versatility.
- Applications: Liquid detergents, shampoos, household cleaners.
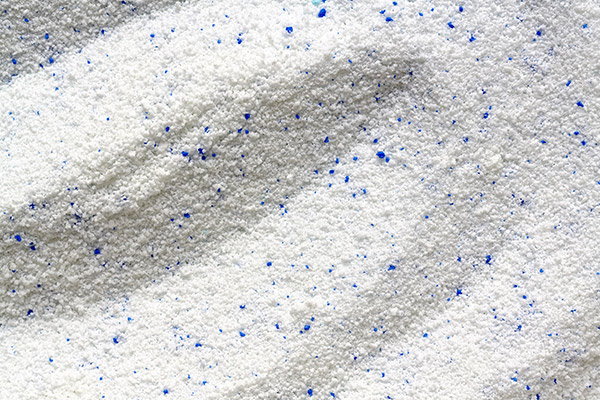

Powdered Surfactants
- Advantages: Long shelf life, easy to transport and store.
- Applications: Powdered detergents, industrial cleaners, some personal care products.
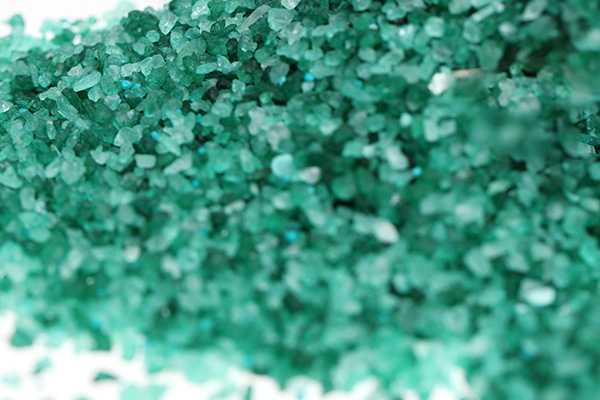

Granular Surfactants
- Advantages: Controlled dissolution rates, ease of handling.
- Applications: Slow-release agricultural products, specialty cleaning agents.
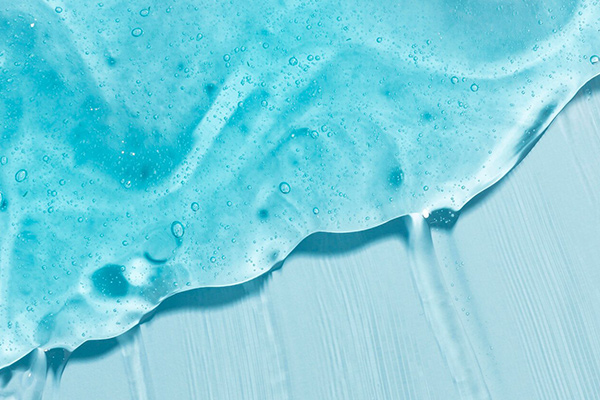

Paste/Gel Surfactants
- Advantages: High concentration, increased stability.
- Applications: Industrial cleaning agents, concentrated personal care formulations.

Solid Surfactants
- Advantages: Stable, convenient for certain product formats.
- Applications: Bar soaps, solid industrial surfactants, some cosmetic products.
Applications of Surfactants
Surfactants are used in a wide range of industries, including but not limited to the following key areas:

Household & Industrial Cleaners
- Products: Detergents, soaps
- Uses: Floor cleaners, window cleaners

Personal Care Products
- Products: Shampoos, body washes
- Uses: Shaving foams, toothpaste

Cosmetics
- Products: Lotions, creams
- Uses: Skincare products

Food Industry
- Functions: Emulsifiers, stabilizers
- Uses: Mix water and oil

Agriculture
- Products: Pesticides, herbicides
- Functions: Dispersing agents, wetting agents

Oil and Gas Industry
- Applications: Enhanced oil recovery
- Functions: Emulsifiers, wetting agents

Textiles and Dyes
- Functions: Wetting agents, dispersing agents
- Uses: Dye uptake, processing
Pharmaceutical Industry
- Functions: Emulsifiers, stabilizers
- Uses: Drug formulations
Get in Touch with Us Now
FAQs
1.What are surfactants?
Surfactants, short for surface-active agents, are compounds that lower the surface tension between two substances, such as liquids, solids, or gases. They contain both hydrophilic (water-attracting) and hydrophobic (water-repelling) parts, allowing them to interact with both oil and water. Surfactants are commonly used in various products such as detergents, soaps, shampoos, and emulsifiers, where they help to remove dirt and oils by allowing them to be dispersed and washed away.
2.What are surfactants used for?
Surfactants are used to enhance cleaning, foaming, and emulsifying properties in various products across industries such as household cleaners, personal care, cosmetics, food processing, agriculture, and oil and gas. They improve the performance and stability of these products, making them more effective and efficient.
3.Are surfactants harmful to humans?
Surfactants can be harmful to humans depending on their type, concentration, and exposure duration. Some surfactants may cause skin and eye irritation, allergic reactions, or respiratory issues. However, many surfactants used in consumer products are formulated to be safe for regular use when following the manufacturer's guidelines. Always handle surfactants according to safety instructions to minimize any potential risks.
4.What is a good surfactant?
A good surfactant effectively lowers surface tension, is stable in various conditions, and is safe for its intended use. It should also be environmentally friendly and compatible with other formulation ingredients.
5.What is a natural surfactant?
Natural surfactants are derived from renewable resources such as plants, animals, or minerals. Examples include soap, derived from natural fats and oils, and saponins, found in certain plants like soapwort and yucca.
6.What is an example of a surfactant?
Sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) is a surfactant widely used in detergents, shampoo, toothpaste, and shower gel. Its significant cleaning and foaming properties can effectively remove surface dirt and grease.
